OPC UA .NET SDK
OPC UA Client- und Serverentwicklung mit C#, VB.NET und C++/CLI

Verwendung
Das OPC UA .NET SDK ermöglicht die Entwicklung von OPC UA Client- und Serveranwendungen gemäß OPC UA v1.03 und höher. Zur Implementierung eines Servers genügt schon die Definition der Datenknoten (siehe unten). Die IP-Adresse und das Transport-Protokoll werden mit den Standardwerten "localhost:4840" und "opc.tcp" festgelegt. Zum Aufbau einer Client-Verbindung genügt die Serveradresse samt Schema des Transport-Protokolls (siehe weiter unten). Für die Entwicklung wird keine Mitgliedschaft bei der OPC Foundation und keine weitere Lizenz als die für Traegers SDK benötigt!
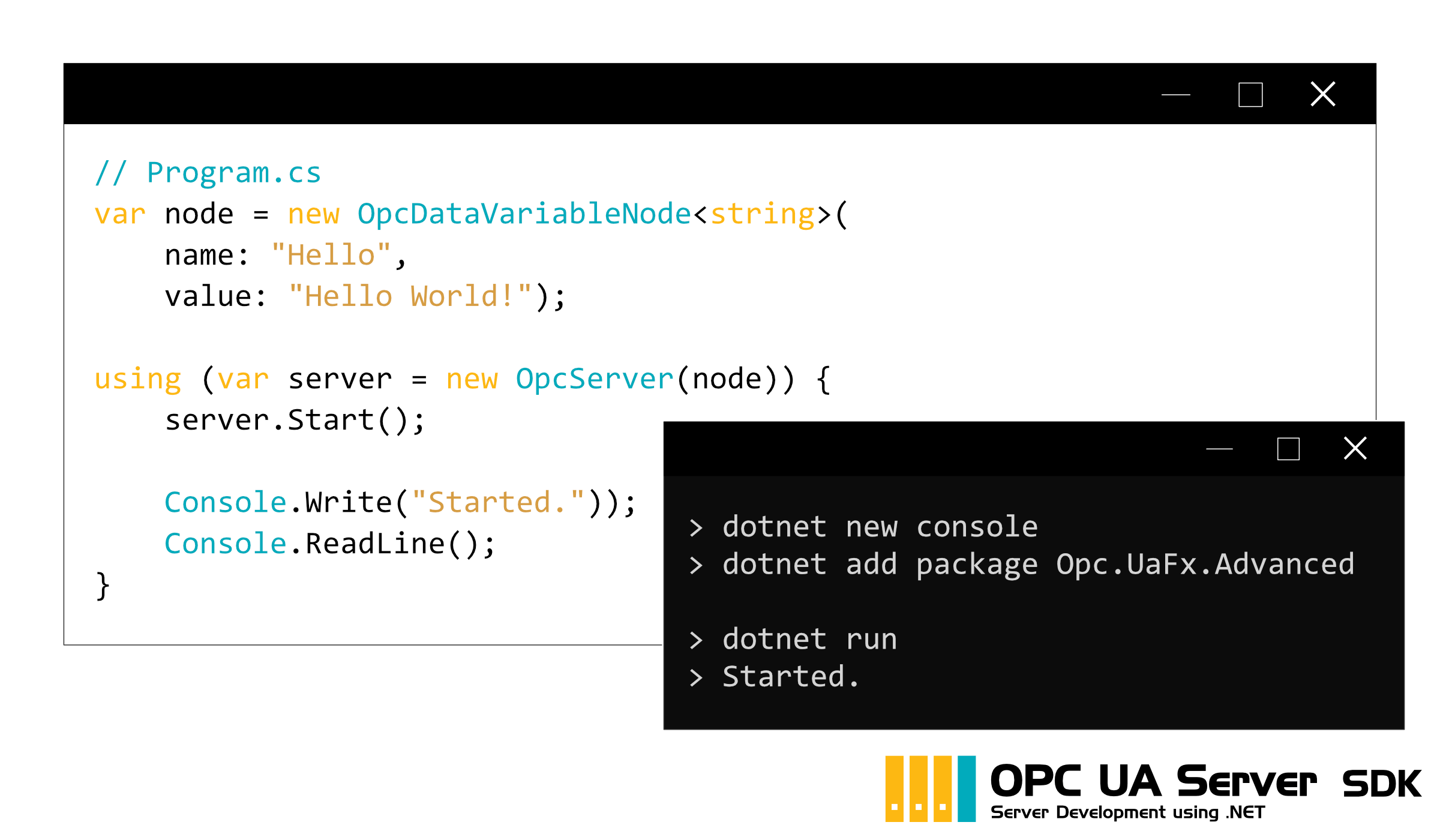
Ein OPC UA Server kann mit ebenso wenigen Zeilen Code realisiert werden, wie ein OPC UA Client. Der oben gezeigte OPC UA Server stellt hier einen Datenknoten samt String-Wert "Hello World!" bereit. Die Bereitstellung der gewünschten Datenknoten funktioniert ohne mehrzeiliges "Node-Setup". Ein OPC UA Client, welcher diesen Datenknoten verarbeitet, zeigt das folgende Beispiel einer OPC UA Clientanwendung.
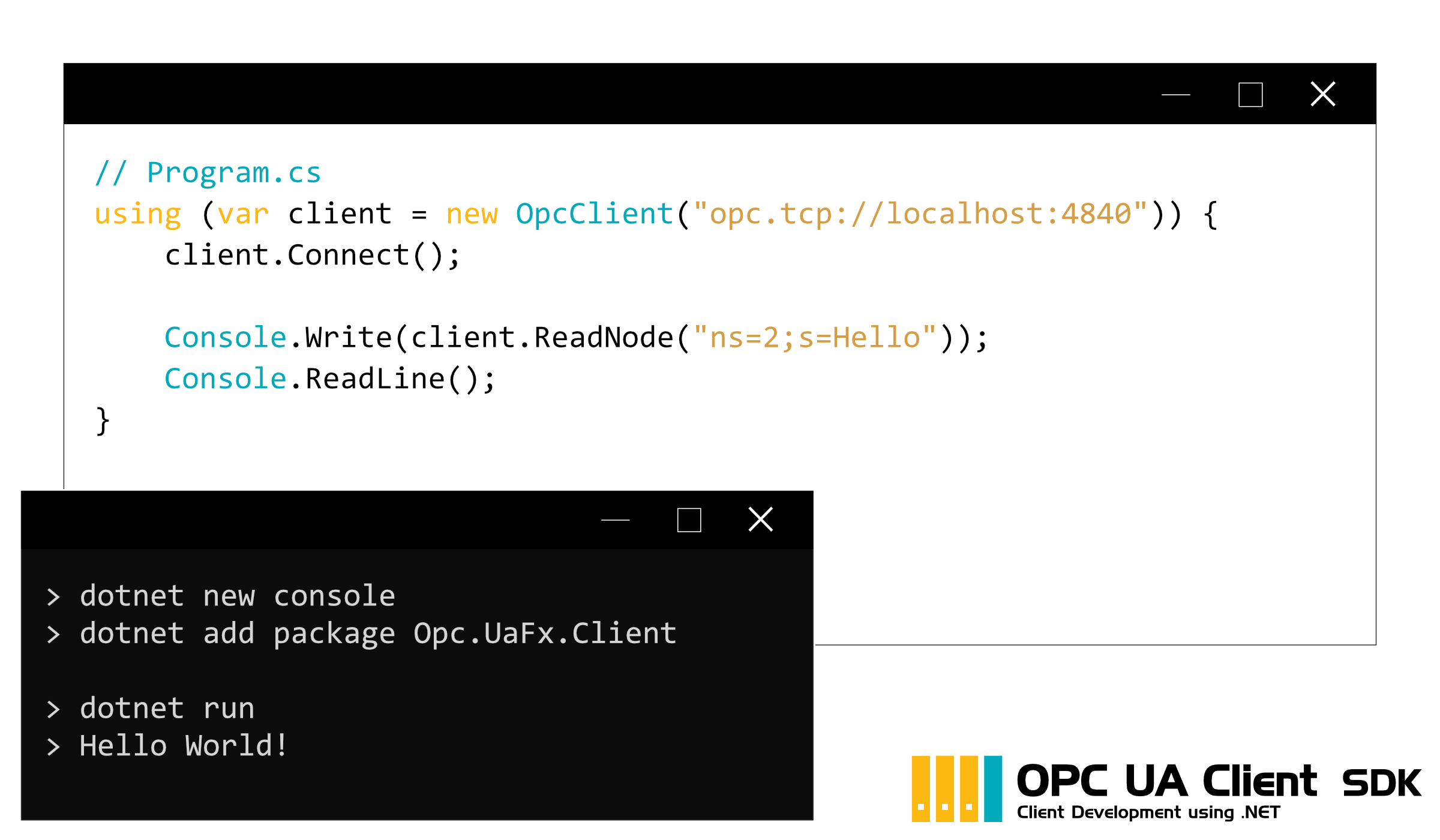
Der Zugriff auf die jeweiligen Datenknoten funktioniert mit gewohnter NodeId Syntax (auch nach optionaler Auflösung über die Browse- und Translate-Dienste). Zur Programmierung kann jede .NET-Sprache wie z.B. C#, VB.NET und C++/CLI verwendet werden. Die Schnittstellen an sich unterscheiden sich nur in Bezug auf die verwendete Programmiersprache.
Vorteile
- Kostenlose Evaluation ohne Registrierung
- Einfache und schnelle Entwicklung
- Industrielle Zuverlässigkeit
- API-Design nach Microsoft Standards
- Royalty-free Lizenzen
- Qualifizierter Support
- Viele Code-Beispiele
- Regelmäßige Updates
- Keine weitere Software erforderlich
- Ohne OPC Foundation Mitgliedschaft verwendbar
Merkmale
- Easy Node Access über BrowseName und NodeId
- Data Access mit Methods, Subscriptions and Files
- Structured Data Types via Name-Value Paare, .NET Dynamic / Types
- Configuration via Code, XML-File oder Dynamisch
- Alarme, Events und Conditions
- Security Policies: None, Sign & SignAndEncrypt
- Security Algorithm: None, Basic128Ras15, Basic256 & Basic256Sha256
OPC UA API
- Data Client & Server
- Alarm Client & Server
- Event Client & Server
- Historical Data Client & Server
- Discovery Client & Server
OPC UA Profile
- Core Characteristics
- Generic Features
- Data Access (DA)
- Event Access (EA)
- Alarm & Condition (AC)
- Alarm & Events (AE)
- Historical Data Access (HDA)
Unentschlossen?
Es müssen (auch) OPC DA Server angesprochen werden? Das SDK gibt es auch als OPC UA .NET SDK + OPC Classic mit Unterstützung für OPC Classic (bestehend aus OPC DA, OPC HDA und OPC AE)!
Einer Komponente, Steuerung oder Anlage soll mit einem OPC UA Server ausgestattet werden? Ganz ohne Programmierung funktioniert das schnell und einfach mit unserer OPC UA Middleware: Codabix Industrial IoT
Die Daten mehrerer OPC UA Server sollen zusammengeführt, per REST API abrufbar, in eine Datenbank gespeichert, an andere Geräte wietergeleitet oder einfach visualisiert werden? Werfen Sie einen Blick auf unsere OPC UA Middleware: Codabix Industrial Edge
Immer noch unentschlossen? Wir beraten Sie gerne kostenfrei und unverbindlich: Kontaktieren Sie uns jetzt!
Lizenzierung
Unsere Lizenzoptionen – so individuell wie Ihre Projekte. Gestalten Sie Ihre Softwareentwicklung so, wie es für Sie am besten passt. Ob Abo oder Lifetime – unsere Lizenzmodelle bieten Ihnen volle Freiheit, erstklassigen Support und kontinuierliche Updates. Ob einmalig oder flexibel – finden Sie die perfekte Lösung für Ihre Vision. Erfahren Sie mehr über unsere Lizenzmodelle.
Features
- Industrie 4.0 konforme Kommunikation mit ...
Steuerungen, Komponenten und ganzen Anlagen
- Lesen und Schreiben von ...
skalaren Werten, Arrays und strukturierten Datentypen
- Bereitstellen und Veröffentlichen von ...
skalaren Werten, Arrays und strukturierten Datentypen
- Interaktiver Zugriff auf Knoten wie ...
Events, Alarme, Bedingungen, Methoden und Dateien
- Bereitstellen von Knoten für ...
Events, Alarme, Bedingungen, Methoden und Dateien
- Auslesen von Server-Informationen wie ...
Standort, Namespaces, Version, Status und Systemzeit
- Bereitstellen von Server-Informationen wie ...
Standort, Namespaces, Version, Status und Systemzeit
- PDU-Optimierte Zugriffe für ...
hochperformante Kommunikation und konsistenter Daten
- Abbrucherkennung zur Sicherung ...
konstanter Verbindungen durch automatischen Wiederaufbau
- Adressierung aller Datenbereiche mit ...
Bezeichnern im OPC UA NodeId, BrowseName und BrowsePath Format, auch mittels LINQ to Nodes
- Boolsche Werte und numerische Werte von ...
1 bis 8, 16, 32 und 64 Bit Datenlänge – auch als Array und Matrix
- Ganzzahlige Werte mit und ohne Vorzeichen über ...
Byte, Int16, UInt16, Int32, UInt32, Int64 und UInt64 – auch als Array und Matrix
- Gleitkomma-Werte mit einfacher/doppelter Genauigkeit über ...
Float (single) und Double – auch als Array und Matrix
- Datum und Zeitwerte über ...
TimeSpan und DateTime (UTC)
- Zeichen und Zeichenketten über ...
Char bis String – auch über Byte mit eigenem Encoding
- Strukturierte/komplexe Datentypen via ...
dynamischen oder eigenen .NET Typen mit impliziter und expliziter Kodierung
- Unterstützte Sprachen
C#, VB.NET und C++/CLI
- Unterstützte Frameworks
.NET Framework 4.6+, .NET Standard 2.0+, .NET Core 3.1+, .NET 5.0+, .NET 6.0+ und .NET 8.0+
- Unterstützte Laufzeitumgebungen
Microsofts CLR, Mono, Xamarin, UWP und Unity
- Unterstützte Plattformen
Windows, Linux, macOS, Android, iOS und Docker